Why test design techniques?
The aim of testing is to provide advice on quality and risks. To do this, the tester needs to collect information about the
system behaviour. The most important means to achieve this is to execute test cases. The big questions in this context are:
‘Which test cases? How many? And how do we get these test cases?’ Test design techniques play an important part in
answering these questions.
Designing test cases is the vital link between the test strategy and the concrete test cases that are used to implement
that test strategy. This is realised in the context of test assignment to test cases, the theme of which can be
outlined as follows (see figure 1 below):
-
It is not possible to test everything within the confines of the preconditions of time and costs defined in the job
specification. Choices will have to be made as to the lengths one wishes to go to in testing.
-
The more important something is, the more intensive the tests required. Something is very important if its failure
would result in severe damage to
the business or client. This is mapped by means of a risk analysis.
-
A test strategy is used to create an overview of what will be tested and how intensively, such that the risks
defined earlier are covered as dequately as possible.
-
The decisions concerning intensive and less intensive testing are translated to concrete statements about the
targeted coverage.
-
Depending on the available test basis, among other things, appropriate test design techniques are selected to
achieve said coverage.
-
The implementation of these techniques eventually results in the set of test cases that is needed to execute the
test assignment satisfactorily.
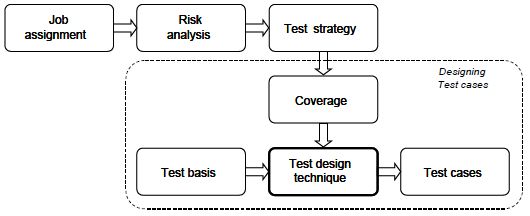
Figure 1: Test design techniques within the context of ‘assignment definition’ to ‘test cases’.
Importance of test design techniques
You will find several arguments below that indicate the importance and benefits of using test design techniques and their
definition in the test specifications.
-
It provides a justified elaboration of the test strategy: the agreed coverage in the agreed place
-
Because a test design technique focuses on achieving a specific coverage to detect specific types of defect (e.g.
in the interfaces, the input checks or the processing), such defects are detected more effectively then by
specifying ad hoc test cases
-
The tests are reproducible because the order and content of the test execution are described in detail
-
The standardised method ensures that the test process is independent of the individual who specifies and executes
the test cases
-
The standardised method ensures that the test specifications are transferable and maintainable
-
It becomes easier to plan and manage the test process because the processes of test specification and execution can
be split up into clearly definable blocks.
|